TELECOMUNICATION AND NETWORK
TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKS
ENTERPRISE NETWORKING A.
UNDERSTANDING ENTERPRISE NETWORKING
According to Manuel Castells, enterprise network is a network formed from some company, or some part of some company, or the internal part of some companies.
One of the characteristics of the enterprise network is a wide-open access network, which allows anyone, be it manufacturers, customers, and hackers & crackers, to determine on-line transactions that occur.
A system is said to be good, including enterprise network, the minimum criteria to be able to answer the following security baseline:
1 Confidentiality
2 Access Control
3 Authentication
4. Integrity
5. Non-repudiation
CONCEPT NETWORK
Two computer when the computer is said to be connected if it can exchange information. The form of the connection does not have to go through copper wire only, but can use a fiber optic, microwave, or satellite.
The concept of a network can be divided into 2, namely:
1 The concept of a network based on the geographical location of
LAN (Local Area Network)
LAN is a computer network that covers only a small area network; such as campus computer network, building, office, home, school or smaller.
MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
A MAN is a network in a city with high speed data transfer, which connects various locations such as campuses, offices, government, and so on. MAN network is a combination of several LANs. The MAN range of between 10 to 50 miles, this MAN is a network that is appropriate to establish a network between offices in the city between the factories / establishments and headquarters that are within his reach.
WAN (Wide Area Network)
WAN is a computer network covering a large area as an example of the computer network between regions, cities or even countries, or can be defined as well as computer networks require routers and public communication channels.
2 Network Topology
Network topology is, things that describe the geometric relationship between the basic elements making up the network, ie nodes, links, and station. The network topology can be divided into 5 main categories as below.
a. The star topology is a form of network topology in the form of convergence of the middle node to any node or user. Star network topology including network topology with medium costs
b. Ring topology is a network topology in which each point is connected to two other points, forming a circular path to form a ring. In a ring topology, data communication can be interrupted if a single point disorder.
c. Bus Topology is the second unjung network must be terminated with a terminator. Barrel connector can be used to extend it. Network consists of only one cable channel that uses a BNC cable. Computer you want to connect to the network can link himself with mentap Ethernetnya along the cable. Linear Bus: This layout includes a common layout. One main cable connects each node, a single channel to access the computer end on end. Each node is connected to two other nodes, except the engine at one end of the cable, each of which is only connected to one other node.
d. Mesh topology implement fully the relationship between central. The number of channels must be provided to form a mesh network is a central number minus 1 (n-1, n = number of central). The complexity of the network is proportional to the increasing number of central installed. Thus besides less economical also relatively expensive to operate.
e. The tree topology is also called multilevel network topology. This topology is usually used for the interconnection between different central denganhirarki. For lower hierarchy depicted on the location of the low and the higher up the hierarchy have. This type of network topology is suitable for use in a computer network system.
Picture Network Topology
Role of Intranet and Extranet.
INTRANET
Intranet is a private network that uses Internet software and TCP / IP protocol. Intranet provides easy access for employees to obtain information company. Intranet is an effective medium to send information about the enterprise applications, such as policies, procedures, and forms of human resources; telephone directory organization; training programs; search engines; customer database; product catalog and manual labor; groupware; organizational chart; the latest news about the organization; warning of crises; as well as access data warehouse and decision support.
EXTRANET
Extranet is a private network that uses Internet technology and the public telecommunication system to establish a secure connection between suppliers, vendors, partners, customers and other business parties in order mendukng business operations or accessing information bisnis.Extranet can be used to exchange data with a large volume using EDI (Electronic Data Interchange), a wide range of catalog products with merchants, cooperation with other companies in the joint venture pengembangkan, providing services by a company against a number of companies in the group, sharing information intended specifically for the corporate partner companies.
B. ALTERNATIVE TELECOMMUNICATIONS NETWORK
Telecommunications is a technique that is capable of changing the information technology system. It is important for users to understand some of the important characteristics of the basic components of the telecommunications network. It can help users to effectively participate in making decisions regarding alternative telecommunications.
Telecommunication line can be interpreted as a form of data and telecommunications are transmitted between the sender and receiver in a telecommunication network.
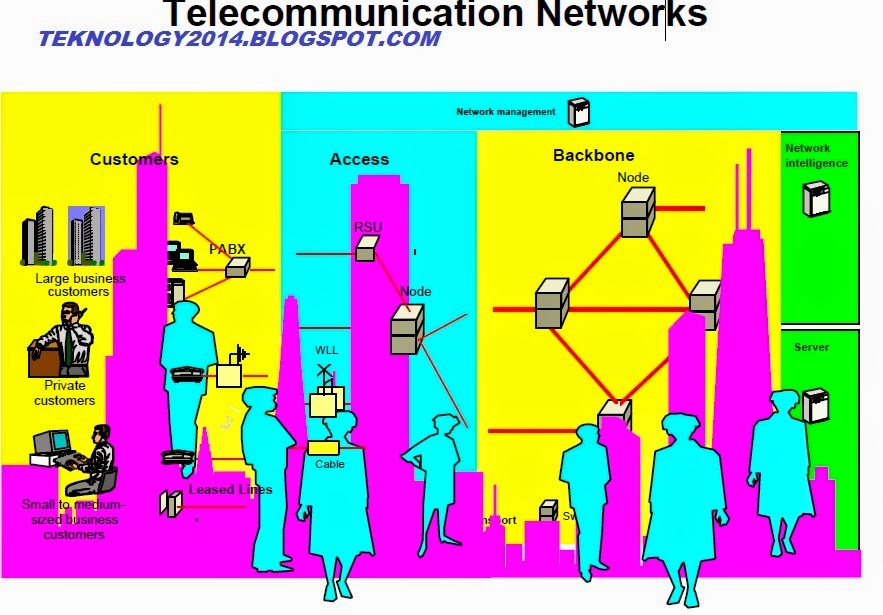
TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK MODEL
In telecommunications umumjaringan some settings where the sender sends the message to the receiver through a channel that consists of several types of medium. Telecommunications enables every person to communicate quickly salaing long distances though.
The image above illustrates the telecommunications network that consists of 5 (five) categories of basic components:
• Terminals
• Telecommunications Processors
• Media and telecommunications channel ends where the data is received and transmitted.
• Computers
• Software control of telecommunications
DIGITAL AND ANALOG SIGNALS
Digital Signal
Is the result of technology that converts the signal into a number one spot combination of the numbers 0 and 1 to process information easily, quickly and accurately. The signal is called a bit.
Analog Signal
The analog signal is the use of electromagnetic waves. Sound delivery process, for example in telephone technology, is passed through electromagnetic waves.
MEDIA TELECOMMUNICATIONS
Types of Telecommunications Media
a) Twisted Pair Wire Cable
This component consists of 2 types, namely Unshielded Twisted-Pair (UTP) and shielded (STP).
- UTP consists of 2,3,4 or more pairs of wires. Each pair of wires twisted 6 times per inch. This is done to avoid electrical and electrical impedance. Sensitive to electrical interference, such as electrical noise by fluorescent lights or elevators berjalan.Kabel this type is also called the IBM cable types 3.
- STP have basically the same characteristics with UTP. Big difference between them lies in the wire and the presence of the insulating sheath that serves to avoid electrical interference.
b) Coaxial Cable
The characteristics of this cable consists of two wires that are covered by the level of isolation 2. The first insulation (insulators in) is the insulation that envelops the solid copper wire. In addition to being protected by an insulator, solid copper wire is also protected by tin foil mounted on insulators, to protect from the effects of electromagnetic fields.
c) Fiber Optic Cable
Fiber Optic has the following characteristics:
The data is sent in the form of light pulses highest transmission speed. Thin and flexible, making it easy to move. Not bothered by the weather and heat.
d) Wireless
Wireless has the characteristics:
Not using a cable, kerna the data transmitted in the form of waves or infrared. Each workstation associated with the hub or concentrator through radio waves or infrared.
TELECOMMUNICATIONS PROCESSOR
There are several kinds of telecommunications processors, such as:
Modem
is a telecommunications processor most commonly used. The modem converts the digital signal from the sender's computer or terminal into analog frequencies that can be transmitted through telephone lines and vice versa convert analog data into digital data. This process is known as modulation and demodulation described by the following picture:
Multiplexer
Multiplexer is a telecommunications processor which allowed the single communications channel to carry data transmissions simultaneously from different terminals. Basically, multiplexers combine the transmission of several terminals at the end of the line that allow telecommunications telekomunikasi.processor tungal communications channel to carry data transmissions from multiple channels simultaneously. Basically multiplexers combine the transmission of several terminals at the end of the telecommunications channel.
Private Branch Exchange (PBX)
Is a communications processor that serve as phone line converter tool in the work area with the local phone company lines. Currently PBX has become an electronic device built in microprocessor and stored therein. Several types of PBX can control the communication around the central area, computer, telecommunications and other processor in a network in an office or other workplace.
ARSITEKTUR JARINGAN ( NETWORK ARCHITECTURE)
NETWORK ARCHITECTURE AND PROTOCOLS
The protocol is a standard set of rules and procedures for controlling communications on the network. These standards are intended only to one course or the equipment manufacturing different types of telecommunications. Part of the purpose of telecommunications network architecture is to create a more standardized and matches between communication protocols.
The purpose of the network architecture is to introduce an open, simple, flexible and efficient telecommunications environment. This would be perfect with the use of a standard protocol. Communication standards that relate directly between hardware and software, and standard design relationship between the user and the computer system.
ALTERNATIVE BANDWIDTH
Quantity that indicates how much data can be passed in via a network connection. Bandwidth or channel capacity information. The maximum ability of a tool to deliver information in units of seconds.
Known also by the difference or interval between the upper and lower limits of a frequency wave transmission in a communication channel. Units used Hertz for analog circuits and digital in units of seconds.
Wideband analog is measured in units of Hertz (Hz) or the second orbit. Digital wideband also refers to the amount or volume of data that is passed through a communication channel is measured in units of bits per second (bps) without involving interference.
The term bandwidth (bandwidth) should not be confused with the term lane (band), such as the cordless phone, for example, operate on track 800MMHz. Path width is the space used on the track. In communications without wiring, size or width of the track to give the impression to the transmission channel. Amount of data that flows through the narrow channel to take a longer period compared to the same amount of data flowing menerusi if the channel is wider.
ALTERNATIVE SWITCHING
Regular telephone connected to circuit switching, where a circuit is introduced for establishing a channel between the sender and receiver and always open up the session / communication section to be complete. In message switching, transmitting a message block (Block) at the same time from switching one to the other. This method is called Store and Forward Transmission. Because the message is transmitted by means of switching before.
Data communication, is communication which is the source of data.
Voice transmissions can be used as the transmission of voice data if the information was changed (encoded) into a digital form.
NETWORK Interoperability
Network Interoperability is the continued ability to send and receive data interconnection between networks provide a level of quality expected by end-user customers without any negative impact to the sending and receiving or network.
Specifically: Network Interoperability is the functional inter-operator who worked in between or multi-vendor, multi-carrier inter-connections (ie, node-to-node, or network-to-network) that works under normal and stress conditions, and per standers applicable, requirements, and specifications



Comments
Post a Comment
Kritik & Saran Anda, Kemajuan Blog Ini... ^_^